Troubleshooting Resistor Failures in Industrial Automation Circuits | Reliability Guide
Troubleshooting Resistor Failures in Industrial Automation Circuits
In industrial automation, reliable circuit performance is critical for production efficiency, safety, and minimizing downtime. Resistors are fundamental components in these circuits, and failures can cause equipment malfunction, production delays, or even safety hazards. Understanding why resistors fail and how to troubleshoot them is essential for engineers, maintenance technicians, and industrial automation specialists.
Understanding Resistor Failures in Industrial Automation
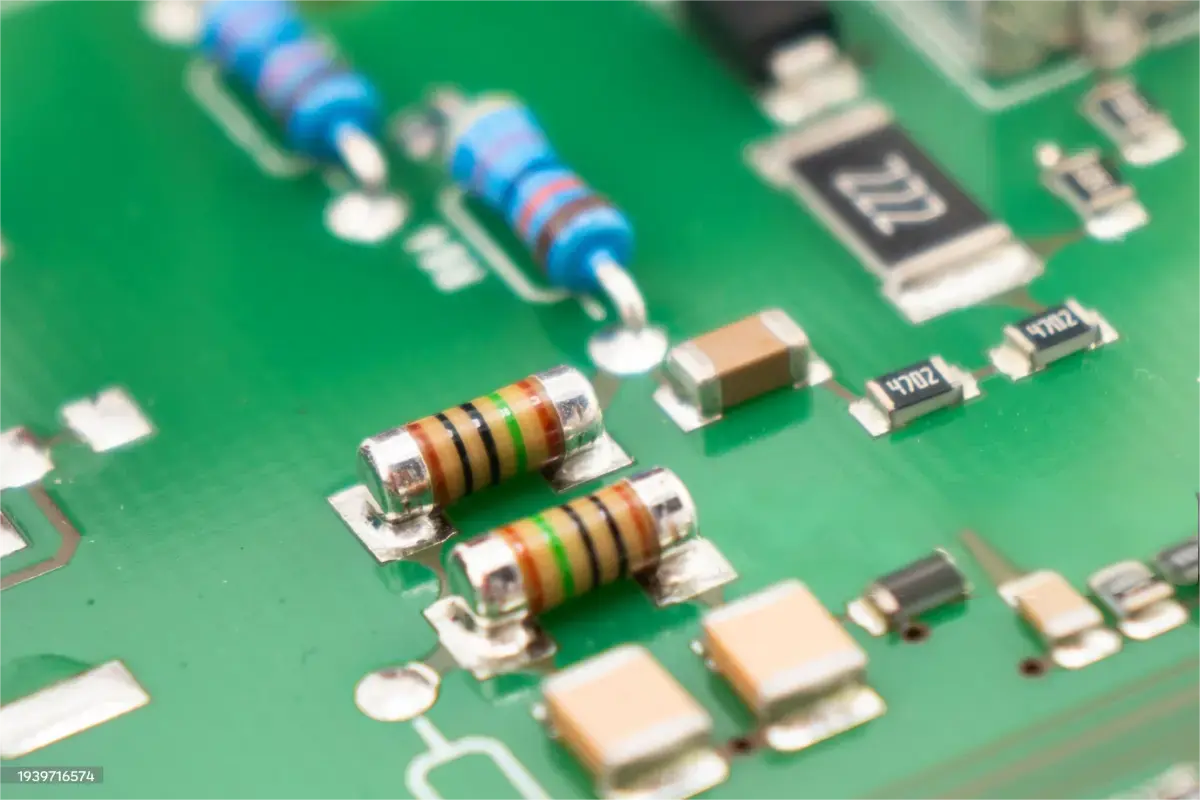
Resistor failures in industrial automation circuits are common yet often overlooked. Factors such as environmental stress, improper design, and electrical overload can compromise resistor performance. These failures can manifest as open circuits, short circuits, drifted resistance values, or intermittent issues.
Common Causes of Resistor Failures
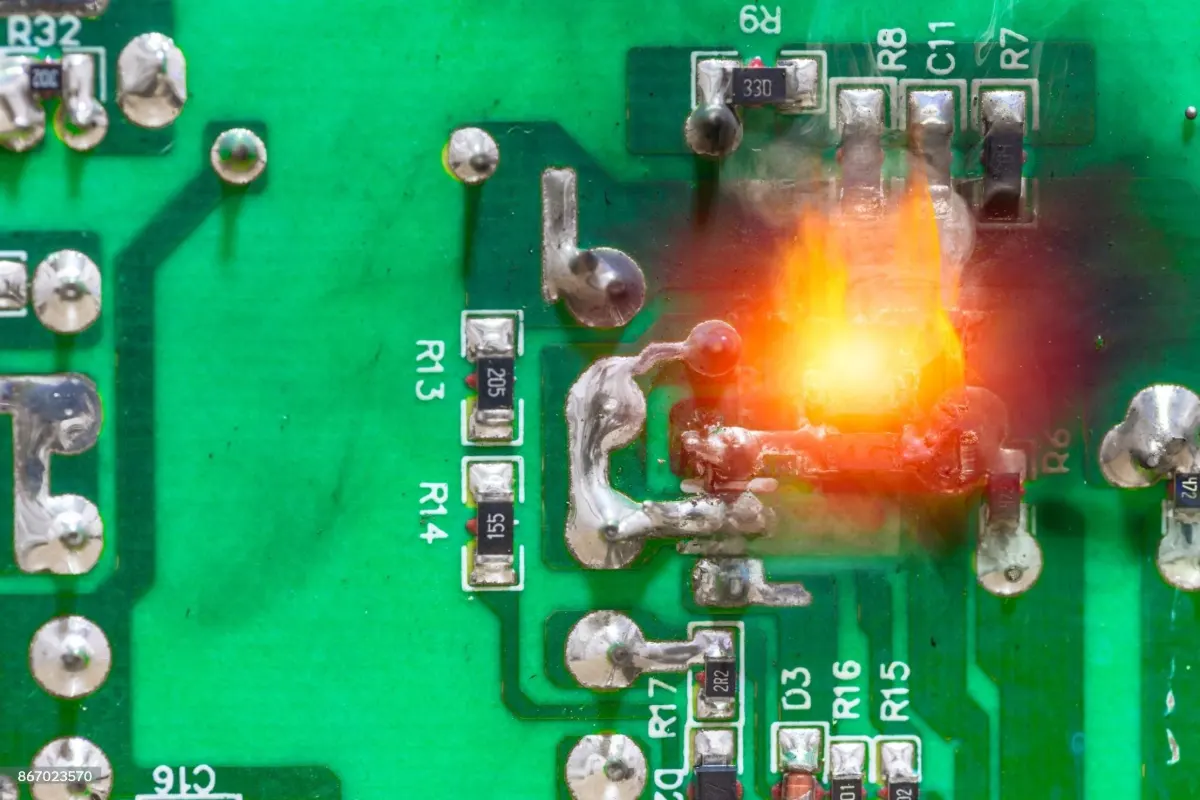
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage: Exceeding a resistor’s rated power or voltage can cause overheating, burning, or thermal runaway.
- Temperature Extremes: Prolonged exposure to high or fluctuating temperatures can degrade materials, causing resistance drift or mechanical failure.
- Mechanical Stress: Vibration, bending, or PCB flexing can crack resistors or their solder joints.
- Environmental Factors: Moisture, dust, and corrosive chemicals can deteriorate resistor coatings or connections.
- Manufacturing Defects: Poor-quality resistors or soldering can lead to early-life failures.
Signs of Resistor Malfunction
- Unexpected circuit behavior or erratic operation
- Visible damage, discoloration, or burn marks on the resistor
- Measured resistance values outside specification
- Frequent tripping of circuit protection devices
Diagnosing Resistor Issues in Industrial Circuits
Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward resolving resistor failures. Industrial automation circuits often involve high currents and complex layouts, so a systematic approach is essential.
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Examine resistors for physical damage, discoloration, cracks, or burnt areas. Look for solder joint issues and check the PCB for signs of overheating.
Step 2: Measure Resistance Values
Using a precision multimeter, measure the resistor value in-circuit (if possible) or after desoldering. Compare measured values with datasheet specifications to identify drift or failure.
Step 3: Thermal Imaging
Infrared cameras can detect hot spots in live circuits. Overheated resistors often indicate overcurrent, poor heat dissipation, or incorrect component selection.
Step 4: Circuit Analysis
Review the circuit design to ensure that resistors are correctly rated for power, voltage, and tolerance. Check for transient spikes, voltage surges, or unbalanced loads that can cause repeated failures.
Preventing Resistor Failures in Industrial Automation
Prevention is more effective than troubleshooting. Proper component selection, circuit design, and maintenance strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of resistor failures.
1. Correct Component Selection
- Choose resistors with appropriate power rating and voltage rating.
- Consider temperature coefficient and environmental conditions.
- For high-reliability applications, select resistors with low tolerance and proven stability.
2. Proper Circuit Design
- Ensure adequate heat dissipation through layout and spacing.
- Use series or parallel resistor networks to distribute load if necessary.
- Include surge protection and current-limiting mechanisms.
3. Environmental Protection
- Apply conformal coating to resistors in harsh environments.
- Maintain humidity and temperature within operational limits.
- Use vibration-resistant mounting techniques for industrial machinery.
4. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
- Schedule periodic inspections and resistance measurements.
- Use predictive maintenance tools like thermal imaging or circuit monitoring sensors.
- Replace aging or stressed resistors before failure occurs.
Case Studies and Practical Insights
Several industrial automation facilities have improved system reliability by addressing resistor failures systematically:
- Motor Control Systems: Replacing undersized wirewound resistors with higher power-rated versions reduced overheating incidents by 70%.
- Power Supplies: Implementing surge protection and thermal monitoring prevented repeated resistor burnout in SMPS circuits.
- Assembly Lines: Introducing regular visual inspections and predictive maintenance reduced unexpected downtime due to resistor failures.
Long-Term Strategies for Reliability
For industrial automation professionals, building a culture of proactive maintenance and component optimization is key:
- Maintain a database of resistor performance and failure history.
- Integrate high-reliability components in new designs.
- Train maintenance staff to identify early signs of resistor issues.
- Use automated monitoring tools to track temperature, current, and voltage stress on critical resistors.
Conclusion
Resistors may seem like simple components, but their failure can disrupt industrial automation systems significantly. By understanding the common causes of resistor failures, employing systematic diagnostic methods, and implementing preventive strategies, engineers can enhance system reliability, reduce downtime, and optimize operational efficiency. Incorporating high-quality components, proper circuit design, and regular maintenance ensures that your industrial automation circuits perform consistently and safely.
Related Resources