How to Choose the Right Smart Meter Shunt for Your Energy Meter Applications
Smart meters rely on high-precision current shunts to ensure accurate energy measurement and billing. Choosing the right smart meter shunt can significantly impact performance, reliability, and compliance. This guide provides a detailed understanding of how to select the proper manganin shunt resistor for your application — from material choice to welding methods and long-term stability.
1. What Is a Smart Meter Shunt?
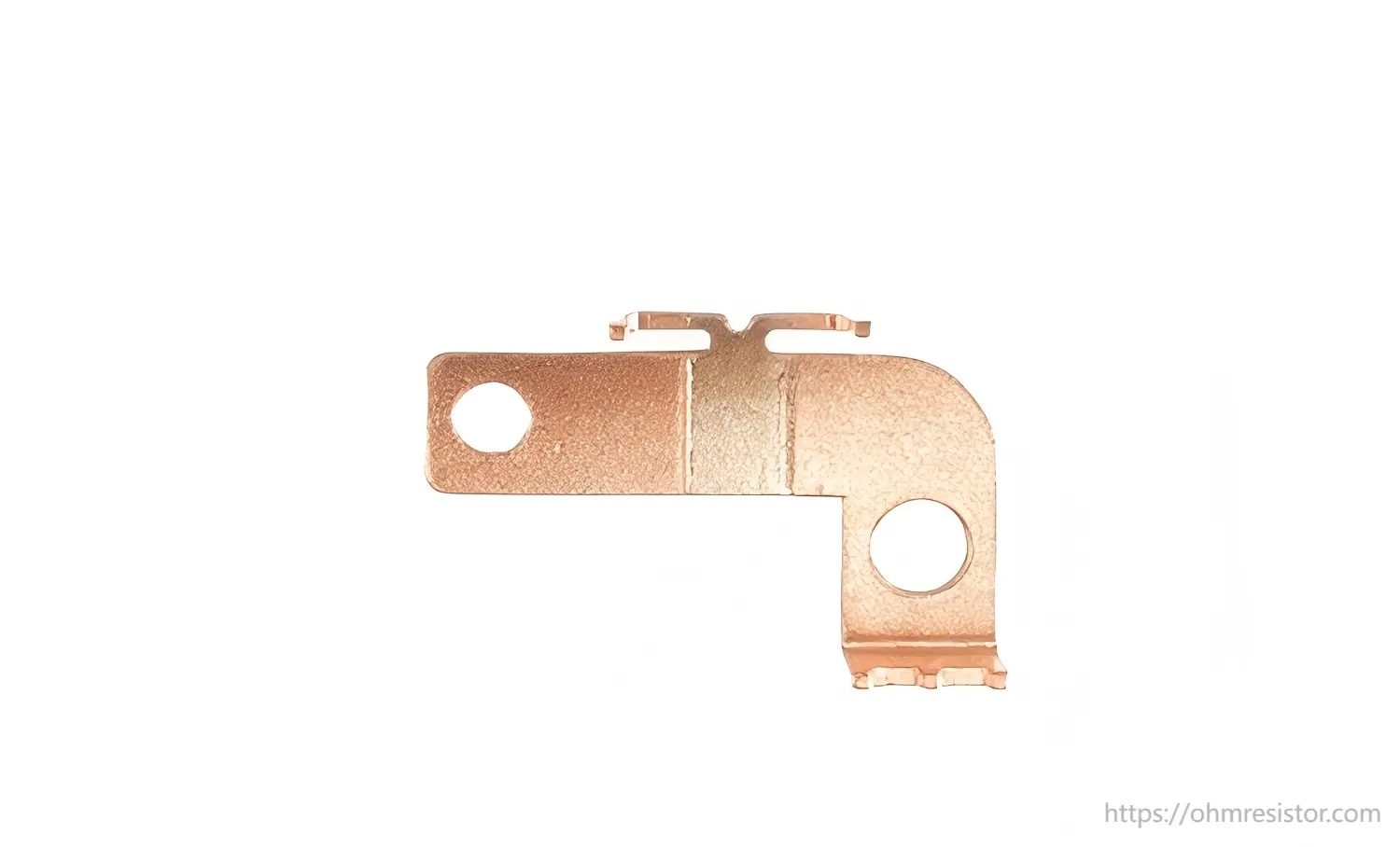
A smart meter shunt is a low-resistance precision component designed to measure current by detecting the small voltage drop across it. It is commonly used in AC/DC energy meters, power analyzers, and EV chargers. The voltage drop is then converted into a digital signal by the measurement IC, allowing for accurate energy consumption tracking.
1.1 How It Works
When current flows through the shunt, a proportional voltage is generated according to Ohm’s law (V = I × R). The energy meter’s ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) samples this voltage, and the microcontroller calculates current and power data in real time.
1.2 Key Benefits
- High measurement accuracy (up to ±0.1%)
- Stable performance across temperature variations
- Compact and cost-effective compared to current transformers (CTs)
- Ideal for both single-phase and three-phase smart meters
2. Material Matters: Why Manganin Is the Best Choice
The performance of a current shunt depends heavily on its material. Among several options, Manganin alloy (Cu86Mn12Ni2) is widely used due to its exceptional thermal and electrical stability.
2.1 Manganin vs. Other Materials
| Material | Temperature Coefficient (ppm/°C) | Stability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manganin | ±15~25 | Excellent | Medium |
| Constantan | ±40~50 | Good | Low |
| Copper | ±3900 | Poor | Low |
2.2 Advantages of Manganin Shunts
- Very low temperature drift ensures precise readings over wide temperature ranges.
- High resistance stability over time, reducing recalibration frequency.
- Excellent long-term reliability under high current load conditions.
3. The Importance of E-Beam Welding in Shunt Manufacturing
For modern smart meter current shunts, Electron Beam (E-Beam) Welding is the preferred method of joining Manganin elements to copper terminals. It ensures metallurgical bonding with minimal thermal stress and excellent conductivity.
3.1 Why E-Beam Welding?
- Creates a clean, oxide-free joint with extremely low contact resistance.
- Prevents performance degradation due to thermal oxidation.
- Improves repeatability and ensures consistent electrical characteristics across batches.
3.2 Comparison: E-Beam Welding vs. Soldering
| Feature | E-Beam Welding | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Resistance | Extremely low | Higher due to flux residues |
| Temperature Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Medium |
4. Key Parameters to Consider When Selecting a Smart Meter Shunt
4.1 Resistance Value (mΩ Range)
Choose a resistance value that balances power loss and voltage sensitivity. Typical ranges are between 50 µΩ and 100 mΩ. For example, 75mV output at rated current is common in metering circuits.
4.2 Rated Current & Power Dissipation
Ensure the shunt can handle the maximum current without overheating. Look for derating curves and ensure power dissipation is within safe limits.
4.3 TCR (Temperature Coefficient of Resistance)
Low TCR (< ±25 ppm/°C) minimizes drift under temperature fluctuations, essential for outdoor meters.
4.4 Tolerance & Accuracy
High-end meters often require ±0.1% or better tolerance. Cheaper models may accept ±1% accuracy.
4.5 Mechanical Design
Consider terminal type (screw, blade, or wire), mounting holes, and overall dimensions for easy integration into the PCB or terminal block.
5. Common Application Scenarios
- Residential single-phase smart meters (5A–60A range)
- Commercial and industrial three-phase meters
- Solar inverters and battery energy storage systems
- EV charging stations and DC metering modules
6. Compliance and Quality Considerations
Though smart meter shunts are not as heavily regulated as automotive parts, high-end OEMs still expect compliance with standards like IEC 62053 and ISO 9001. Choosing a supplier with automated E-beam welding lines, 100% resistance inspection, and traceable lot control ensures long-term reliability.
To learn more about global smart metering standards, visit the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) website.
7. Conclusion: Precision Begins with the Right Shunt
Choosing the right smart meter shunt is a balance between precision, material stability, and cost efficiency. A Manganin E-beam welded shunt offers the ideal combination of accuracy and durability, making it the industry standard for smart metering applications.
Whether you are designing a new energy meter or optimizing an existing one, selecting a trusted supplier and well-engineered shunt will directly determine your meter’s performance and lifespan.
For more details or custom solutions, contact our technical team for a consultation.