How Different Configurations of Current Sense Resistors Affect Performance
Introduction
Current sense resistors play a vital role in precise current measurement across a wide range of electronic applications—from power supplies to motor controls. However, the configuration of these resistors within a circuit can dramatically impact their performance, accuracy, and reliability. This article explores the most common configurations and how each affects the overall system.
⚡ High-Side vs. Low-Side Sensing
High-Side Sensing
Placed between the power supply and the load.
Offers better fault detection and system protection.
Requires a more complex design due to higher common-mode voltage.
May introduce challenges for low-voltage signal processing.
Low-Side Sensing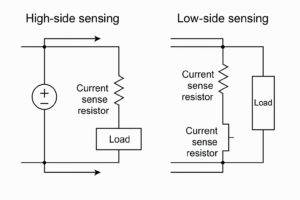
Positioned between the load and ground.
Simpler and less expensive to implement.
However, it may not detect certain faults, and can introduce ground disturbances.
📌 Design Tip: Choose high-side sensing for safety-critical applications and low-side for simple cost-sensitive circuits.
🧲 Impact of Kelvin Connections
Kelvin (4-terminal) connections separate the current path and voltage sensing path, which greatly improves measurement accuracy.
Benefits:
Reduces error due to PCB trace resistance.
Enhances precision in low-ohm resistor designs (e.g., <1 mΩ).
Ideal for high-current or precision current sensing applications.
🌡️ Thermal Management and Placement
Resistor placement near heat-generating components can lead to resistance drift.
Good layout design minimizes self-heating effects and enhances stability.
Use resistors with low TCR (Temperature Coefficient of Resistance) for consistent results under load.
📶 EMI and Parasitic Effects
High-frequency switching circuits may induce EMI in the sense lines.
Long traces and poor layout can cause parasitic inductance, distorting fast transient measurements.
Shielded traces and proper ground referencing help mitigate noise issues.
✅ Conclusion
The performance of current sense resistors is not only defined by their material and size, but also how and where they are implemented in a circuit. Choosing the right configuration—be it high-side, low-side, or Kelvin-sensed—can significantly affect your system’s accuracy, thermal stability, and EMI robustness.
For high-precision applications, always evaluate configuration trade-offs during the design phase. The right setup ensures safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting electronic systems.